Hair Loss: Understanding the Causes of Baldness
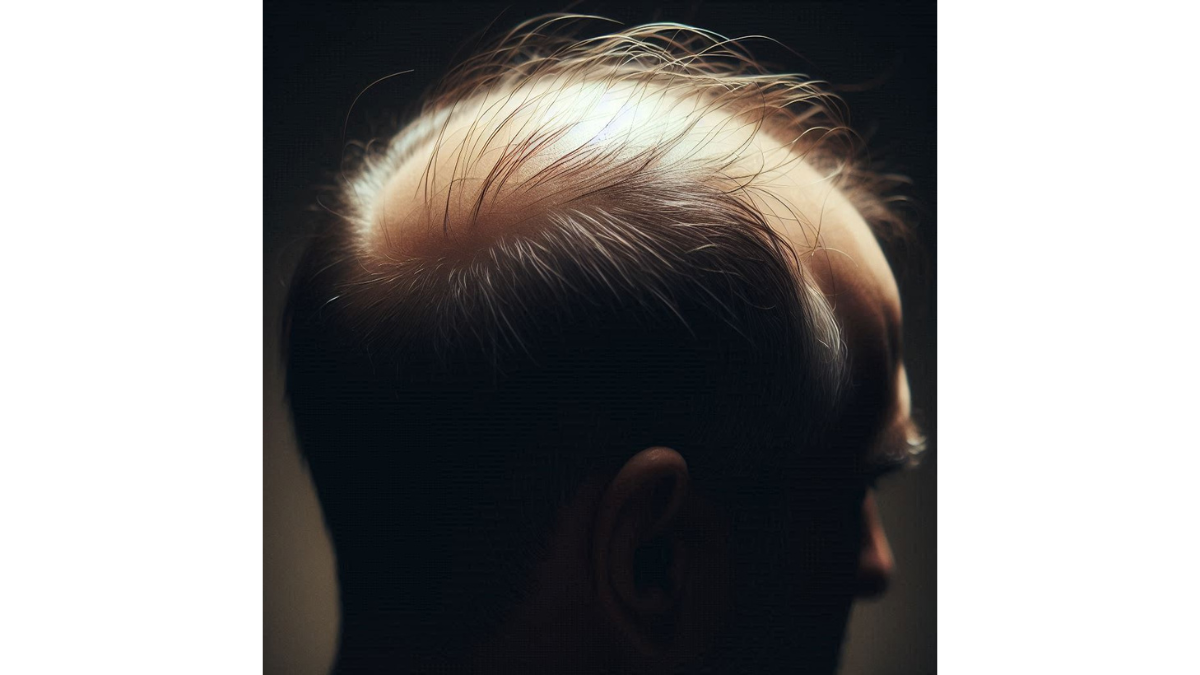
Hair Loss: Understanding the Causes of Baldness – Hair loss is a common issue that many individuals, regardless of age or gender, face at some point in their lives. It can be an emotional and distressing experience, leading to dips in self-esteem and confidence. In fact, a study revealed that almost 40% of men and 50% of women will notice some degree of hair loss by the time they reach 50. When it comes to understanding the science behind hair loss, it’s essential to recognize that it isn’t just a singular issue but a complex interplay of various factors. Conditions such as androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male or female pattern baldness, are well-documented, but there are also many other contributors that can result in thinning hair or bald patches.
These can include hormonal imbalances, scalp health, and even nutritional deficiencies. So what does the science say? Hair grows in cycles, with a growth phase, a transitional phase, and a resting phase. Problems arise when there is an imbalance—whether that be genetic, hormonal, or environmental—that disrupts this natural cycle, ultimately leading to hair loss. For those who have struggled with hair loss, the psychological impact can be profound. Take Sarah, for example. Noticing her hair thinning in her twenties, she felt a significant shift in her confidence. “Every time I looked in the mirror,” she shared, “I couldn’t see the person I used to be. It was as if my identity was slipping away along with my hair.” Stories like Sarah’s echo the feelings of countless individuals dealing with hair loss, making it a topic deserving of thorough exploration.
Importance of Understanding Baldness Causes
Understanding the causes of baldness is crucial—not just for prevention but also for empowerment. You might be asking yourself: “Why should I delve into the science behind my hair loss?” The reality is that awareness equips you with the knowledge to make informed decisions regarding treatment options. Below are some reasons why understanding these causes is essential:
- Tailored Solutions: By knowing the root cause of your hair loss, you can choose the right remedies, whether they be topical treatments, lifestyle changes, or medical interventions.
- Early Intervention: Recognizing the symptoms and causes of hair loss early on can lead to more effective treatments. For example, nutritional deficiencies may be easier to rectify than a genetic predisposition.
- Emotional Resilience: Understanding that you are not alone in this journey can build resilience. Many people go through similar struggles, and connecting with others can provide emotional support.
- Preventive Measures: Once you understand what contributes to baldness specifically for you, it becomes much easier to implement preventive measures. For instance, if hormonal imbalance is a factor, regular check-ups could guide effective management.
So while it might seem overwhelming at first glance, please remember that education can be incredibly liberating. Just like how Sarah decided to take proactive steps to analyze her hair loss, you too can embark on this journey. You can consult with dermatologists, explore specific treatments, and invest in hair health—all while having a clearer comprehension of what’s happening beneath the surface. As we delve deeper into the multifaceted nature of hair loss in the subsequent sections, keep in mind that knowledge is power, and your journey to understanding the causes of baldness can set the groundwork for effective solutions. Together, let’s navigate through this intricate web of factors that contribute to hair loss, and empower you to take control of your hair health.
Genetics and Baldness
Role of Genetics in Hair Loss
As we dive deeper into the science behind hair loss, we can’t ignore the significant role genetics plays in this journey. It’s fascinating to think about how your family history may shape your relationship with your hair. For many, the journey of hair loss often reflects the story of past generations. Genetic hair loss is most commonly associated with androgenetic alopecia, which can affect both men and women. This condition doesn’t discriminate; it can appear as receding hairlines in men or thinning hair at the crown in women. According to research, about 80% of men and around 50% of women will experience some degree of hair loss due to genetic factors at some point in their lives. But how does this work?
The hair follicles on your scalp are sensitive to a hormone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT) which is derived from testosterone. In those who are genetically predisposed, follicles gradually shrink and produce thinner hair over time. The result? Thinning hair or bald patches. Think of it this way: if you’re like Tom, who inherited his grandfather’s signature hairline, you may also be dealing with a receding hairline in your adulthood. “I never wanted to believe I’d end up like my dad and granddad,” Tom humorously reflects. “But here I am, staring at the mirror, confirming the family tradition!” Recognizing this hereditary pattern can be both humorous and alarming! In understanding how significantly genetics contributes to hair loss, consider these key takeaways:
- Familial Patterns: Pay attention to your family history. Observing whether your close relatives experienced hair loss can give you crucial insight into your own risk.
- Mixed Genetics: It’s essential to note that hair loss is polygenic; this means multiple genes contribute to the condition. Thus, the combination of genes inherited from both parents plays a pivotal role.
- Age Factor: While genetics is a significant contributor, age is also a factor. The likelihood of experiencing genetic hair loss increases as one gets older, regardless of family history.
Hereditary Factors Contributing to Baldness
Now that we’ve examined the integral role of genetics, let’s take a closer look at some hereditary factors that contribute to hair loss. Understanding these factors equips you with the knowledge to anticipate changes and potentially seek preventive solutions.
- Gender:
- Men are generally more affected by hereditary hair loss than women, attributed to the powerful influence of androgens in males.
- Women often observe thinning uniformly, rather than the defined bald spots seen in men.
- Inheritance Patterns:
- While many believe that the gene for baldness is inherited from one’s mother, studies suggest that it may come from both sides of the family. Traits found on the X chromosome (inherited from mothers) and various autosomal chromosomes contribute to male pattern baldness.
- Age of Onset:
- If your family members started losing hair in their late twenties or early thirties, the likelihood of you experiencing similar changes in that timeframe is heightened.
- Early onset can indicate stronger genetic influence, meaning proactive measures could be beneficial sooner rather than later.
- DHT Sensitivity:
- Individuals possess different levels of sensitivity to DHT. Research suggests that some people are genetically predisposed to develop more sensitive hair follicles. This can accelerate hair loss among those with such sensitivity.
- Associated Conditions:
- Certain conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in women, or hormonal imbalances—often hereditary—can play a role in hair loss. If health conditions run in families, it may be worth investigating their implications on your hair.
Understanding these hereditary factors can guide your next steps if you begin to notice changes in your hair. For Tom, embracing his family legacy means taking a proactive approach—whether that’s consulting a specialist or researching hair care routines tailored for his condition. In the next sections, we will further navigate the intricate web of causes behind hair loss, including the influences of hormonal imbalances and scalp health. As you begin to piece together your unique narrative with hair loss, remember—you’re not alone in this journey. Armed with knowledge about your genetic predisposition, you can take informed actions and explore effective treatments. Let’s continue to unravel the layers together!
Hormonal Imbalance
Impact of Hormones on Hair Growth
Continuing our exploration of hair loss, we now turn our attention to hormonal imbalance—a significant player in the science behind baldness. Hormones function as chemical messengers in the body, influencing a myriad of physiological processes, including hair growth. Each strand of hair grows in a cycle that’s tightly regulated by hormones; any disruption in this delicate balance can lead to thinning hair or even bald spots. One of the most influential hormones in hair loss is androgens, particularly testosterone and its derivative dihydrotestosterone (DHT). As we learned previously, sensitivity to DHT can cause hair follicles to shrink and shorten the hair growth cycle—ultimately leading to hair loss. But it’s not just androgens at play. Other hormones like estrogen, progesterone, and thyroid hormones also significantly affect the hair growth cycle. Let’s break it down:
- Estrogen: This hormone is known for promoting hair growth in women. During pregnancy, when estrogen levels are elevated, many women notice their hair becomes thicker and fuller. Conversely, after childbirth, estrogen levels plummet, sometimes resulting in postpartum hair loss.
- Thyroid Hormones: An underactive or overactive thyroid can wreak havoc on hair growth. Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism and influence the hair growth cycle as well. Those with hypothyroidism often notice hair thinning as part of the condition.
Consider Emily’s experience. After the birth of her child, she walked away from the experience with a new bundle of joy but also new challenges—like noticeable patches of hair loss. “It was alarming, and I wished someone had warned me about postpartum hair loss,” she reflects. Through consultation with her doctor, she learned how hormonal changes post-pregnancy were impacting her. Furthermore, cortisol—a hormone produced during stress—can also affect hair health. Chronic stress often results in elevated cortisol levels, leading to a condition commonly referred to as telogen effluvium, which can cause hair to shed more than usual.
Key Points on Hormones and Hair Growth:
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Changes in hormones during life stages (e.g., puberty, pregnancy, menopause) can induce hair loss.
- DHT Sensitivity: High DHT levels are linked to genetic predisposition concerning hair loss.
- Cortisol Levels: Manage stress effectively to keep cortisol levels in check, which can help prevent hair loss.
Hormonal Disorders Linked to Baldness
Moving forward, it’s vital to recognize that several hormonal disorders are frequently linked to hair loss. Understanding these conditions can help you identify potential culprits behind your own hair troubles.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
- PCOS is a hormonal disorder common among women of reproductive age and is often characterized by an imbalance of hormones like estrogen and testosterone.
- Higher levels of male hormones can lead to hair thinning or excess hair growth in unwanted areas.
- Hypothyroidism/Hyperthyroidism:
- As mentioned earlier, an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) can reduce hair growth. In contrast, hyperthyroidism can also result in hair thinning or shedding.
- These conditions can be diagnosed through blood tests measuring thyroid hormone levels.
- Cushing’s Syndrome:
- Caused by prolonged exposure to high cortisol levels, Cushing’s syndrome can lead to various symptoms, including hair loss.
- This can stem from prolonged use of corticosteroid medications or conditions that cause the body to produce excess cortisol.
- Menopause:
- An inevitable life stage that brings a dramatic hormonal shift can contribute to thinning hair. Many women will notice this during and after menopause, often due to decreased estrogen levels.
- This common transitional period emphasizes the importance of maintaining a balanced lifestyle to support hair health.
Understanding these associations with hormonal imbalances can empower you in addressing your hair loss. If you suspect a hormonal issue could be contributing to your thinning hair, a consult with a healthcare professional can help pave the way to effective treatment. In the upcoming sections, we will explore the significance of scalp health and its role in hair growth. By delving into these interconnected areas, we can connect the dots and foster your understanding of maintaining healthy, thriving hair. Let’s keep moving forward on this enlightening journey together!
Scalp Health
Importance of Scalp Care for Preventing Hair Loss
As we navigate through the complexities of hair loss, it’s essential to shine a light on an often-overlooked aspect: scalp health. The relationship between your scalp and hair growth is deeply intertwined, just like the roots of a plant need healthy soil to thrive. If the scalp isn’t well cared for, not only can it lead to uncomfortable conditions, but it can also significantly affect hair growth and overall health. Just like our facial skin, the scalp requires regular maintenance. If you think about it, your hair grows directly from the scalp. Taking care of it is crucial for sustaining healthy hair. Regular scalp care can prevent various issues that lead to hair loss. Here are several reasons why you should prioritize your scalp health:
- Fostering Hair Growth: A clean, well-moisturized scalp promotes better blood circulation, which nourishes hair follicles and leads to more robust hair growth.
- Reducing Build-Up: Products like gels, sprays, and oils can accumulate on your scalp, leading to clogged hair follicles. Regular cleansing helps to remove this build-up, allowing hair to grow more freely.
- Balancing Oil Production: Overwashing can strip your scalp of natural oils, while underwashing can cause an oily scalp. Finding a balance is key.
- Preventing Infections: Bacterial and fungal infections can lead to inflammation and hair loss. Comprehensive scalp care can aid in preventing these issues.
Think of Marcus, a friend who loved trying new hair products but didn’t pay attention to his scalp. After a few months, he started to notice itching and a sudden increase in hair shedding. “I had no idea my scalp needed as much love as my hair,” he shared, realizing that a little care could have gone a long way in maintaining both. To keep your scalp healthy, consider the following care tips:
- Regular Cleansing: Use a gentle shampoo that fits your hair type to keep the scalp clean without stripping it of moisture.
- Gentle Massage: When shampooing, consider using your fingers to massage the scalp. This enhances blood circulation and promotes relaxation.
- Exfoliate: Just like your skin, your scalp can benefit from exfoliation to remove dead skin cells and product residue.
- Maintain Hydration: Just as we moisturize our skin, using scalp oils or conditioners can prevent dryness and irritation.
Common Scalp Conditions Leading to Baldness
While proper scalp care is vital for maintaining healthy hair, certain scalp conditions can still pose serious threats to your hair growth. Being informed about these conditions can empower you to take action if you notice any warning signs.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis:
- This common skin condition manifests as greasy, yellowish flakes on the scalp, often resulting in itchiness and inflammation.
- It can lead to hair loss if not treated, as prolonged inflammation can damage hair follicles.
- Psoriasis:
- Psoriasis is characterized by red, scaly patches on the scalp that can extend to the hairline. It’s an autoimmune condition where skin cells multiply rapidly.
- The resultant itching and inflammation can contribute to hair shedding.
- Folliculitis:
- This condition involves the inflammation of hair follicles, often due to bacterial or fungal infections.
- It may lead to painful bumps on the scalp and can cause patchy hair loss if left untreated.
- Alopecia Areata:
- Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder that results in sudden hair loss in circular patches. It can affect the hair on the scalp and other areas of the body.
- Understanding your scalp’s health can help you seek timely treatment for conditions like this.
- Dandruff:
- While often dismissed as a trivial nuisance, dandruff can be a sign of an underlying scalp condition and can lead to flakes and itchiness. Chronic dandruff can aggravate hair loss.
If you find yourself experiencing any of these symptoms, consulting a dermatologist is crucial. Early intervention can often make a profound difference, allowing you to manage or heal from the condition effectively. As we move forward in our discussion on hair loss, let’s shed light on how nutritional deficiencies can also play a role in your hair health. Understanding the complete picture will empower you to address every potential factor contributing to hair loss. Join me as we continue this enlightening journey toward conquering hair loss!
Nutritional Deficiencies
Essential Nutrients for Hair Growth
As we continue our exploration of hair loss, let’s now turn our attention to Nutritional Deficiencies—a critical yet often underestimated aspect of hair health. Our bodies are like finely tuned machines, and just as any engine requires fuel to run smoothly, your hair follicles need specific nutrients to thrive. Hair growth is a complex process involving various biological functions, and good nutrition directly impacts this. Essential nutrients can help not only maintain healthy hair but also promote growth, overall strength, and resilience. Here’s a closer look at some nutrients that play a crucial role in hair growth:
- Proteins:
- Hair is primarily composed of a protein called keratin. Consuming adequate protein is essential for maintaining the strength and structure of hair.
- Aim to include lean meats, fish, eggs, nuts, and legumes in your diet.
- Iron:
- Iron is vital for transporting oxygen to hair follicles, supporting growth and repair. Hair loss can occur when iron levels are low, leading to a condition called telogen effluvium where hair sheds more than normal.
- You can find iron in foods like red meat, leafy greens like spinach, and legumes.
- Vitamins A and C:
- Vitamin A helps regulate sebum production on the scalp, which keeps hair moisturized. It also aids in producing retinoids that promote hair growth.
- Vitamin C is crucial for collagen production, which strengthens hair. It also enhances iron absorption, further promoting hair vitality.
- Citrus fruits, bell peppers, and carrots are excellent sources of these vitamins.
- Biotin:
- This B-vitamin is known to improve hair thickness and promote new hair growth. It has gained popularity in hair-care supplements for its beneficial effects.
- Foods rich in biotin include eggs, nuts, and whole grains.
- Zinc:
- Zinc plays an important role in hair tissue growth and repair, as well as keeping the oil glands around follicles functioning properly. A deficiency can result in hair shedding.
- You can find zinc in seafood, seeds, nuts, and whole grains.
Consider the story of Lisa, who for years struggled with hair thinning without knowing the potential underlying cause. “I thought it was just stress or genetics,” she recalls. After some research and consultations, she decided to adjust her diet. “Once I started adding more protein and vitamins to my meals, I honestly noticed a difference!” This change nipped the hair loss in the bud and revitalized her locks.
Key Nutrients for Preventing Hair Loss:
Lack of Vitamins and Minerals in Relation to Baldness
While we have established the essential nutrients vital for hair growth, it’s equally important to discuss what happens when these nutrients are deficient. A lack of vitamins and minerals can lead to significant hair issues, sometimes culminating in baldness.
- Iron Deficiency:
- When iron levels drop, it disrupts the oxygen supply to the hair follicles, leading to hair loss. Iron deficiency can be particularly common in women during their menstrual periods, pregnancy, or those who have dietary restrictions, making monitoring iron intake essential.
- Biotin Deficiency:
- Though rare, a biotin deficiency can result in thinning hair and brittle strands. If you notice your hair feeling weak despite good care, it may be time to evaluate your biotin levels.
- Vitamin D Deficiency:
- Emerging research suggests that Vitamin D is linked to hair follicle cycling. Low levels of Vitamin D are associated with alopecia areata, a condition leading to patchy hair loss. Natural sunlight is a great way to boost your Vitamin D levels, alongside fatty fish and fortified foods.
- Zinc Deficiency:
- Zinc plays a key role in repairing hair tissue and is crucial for maintaining healthy hair follicles. A deficiency can lead to hair loss as well as slow recovery from scalp inflammation.
- Hormonal Imbalances with Nutrient Deficiencies:
- Sometimes, nutrient deficiencies lead to imbalances in cortisol or other hormones, which can further exacerbate hair loss.
Maintaining a balanced diet and ensuring you’re meeting your nutritional needs is crucial for healthy hair. If you suspect a deficiency may be affecting your hair health, consider consulting a healthcare professional for proper testing and advice. As we wrap this exploration of nutritional deficiencies, it’s clear that the foundation for healthy hair extends beyond just topical products. In our next segment, we will explore practical steps you can take to enhance your hair care routine and health. Let’s keep moving forward as we work towards healthier hair together!
You might also find this article helpful Building a Strong Foundation :Balanced Diet Enhances Your Health





