Gingivitis in Dogs: Causes and Symptoms and Treatment Options
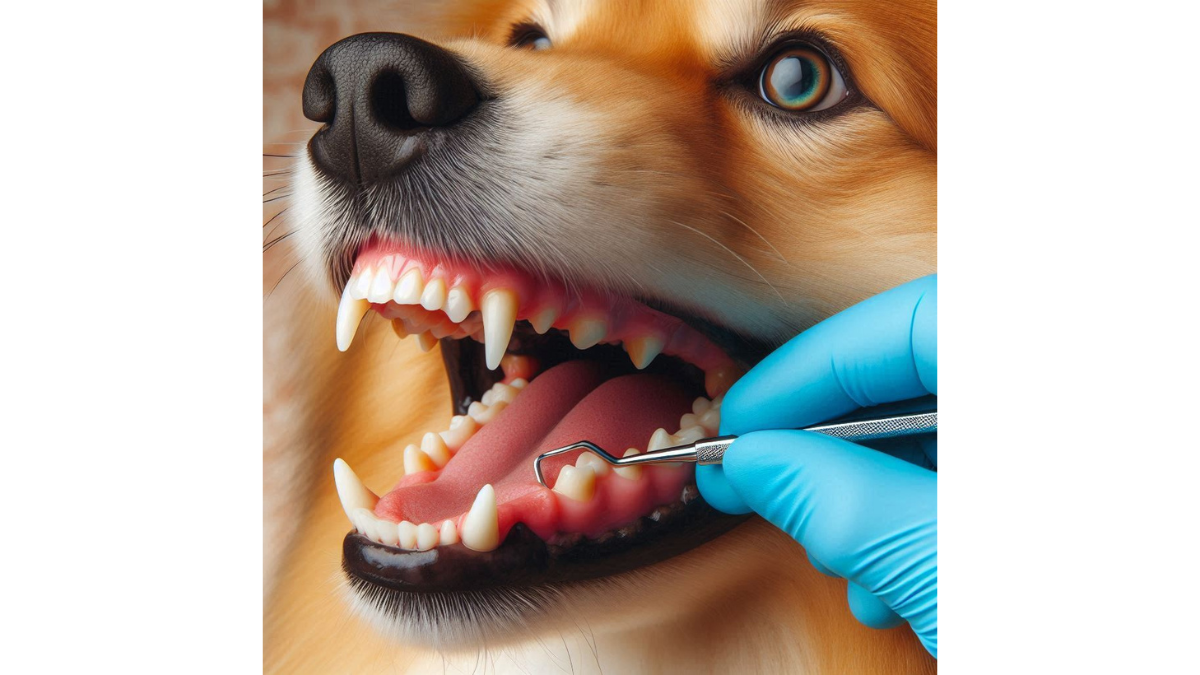
Gingivitis in Dogs: Causes and Symptoms and Treatment Options – Gingivitis in dogs is a common dental condition characterized by inflammation of the gums. It usually arises from the accumulation of plaque, which harbors bacteria that irritate the gum tissue. This condition often presents as a precursor to more severe dental issues, making it crucial for dog owners to recognize and address it early. You might notice your furry friend displaying some unusual behaviors or physical signs. Is your dog suddenly hesitating to chew its favorite toys? Or perhaps you’ve caught a whiff of unpleasant breath when they come in for snuggles? These can be telltale indicators that your dog may be suffering from gingivitis. In a nutshell, gingivitis can lead to more severe conditions, including periodontal disease, if left untreated. Just remember: caught early, it’s manageable!
Importance of Addressing Gingivitis in Dogs
Addressing gingivitis promptly isn’t just about avoiding bad breath; it’s about ensuring your dog’s overall well-being. Here’s why tackling this issue is paramount:
- Health Risks: Untreated gingivitis can escalate into periodontal disease, which doesn’t just affect the mouth but may also lead to systemic health issues. Think about it—bacteria from the mouth can enter the bloodstream, potentially causing problems in organs such as the heart and kidneys.
- Quality of Life: Your dog deserves to enjoy life without the discomfort of oral pain. An inflamed gum may make it difficult for your pet to eat, affecting their nutrition and energy levels.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Early intervention can save you a significant amount in dental treatments down the line. By investing time in your dog’s oral hygiene now, you can avoid more invasive (and expensive) procedures later.
A close friend of mine once had a lovely golden retriever named Max. After noticing a sudden change in his appetite, they discovered he had gingivitis. Fortunately, they acted quickly, and Max made a full recovery. It’s a reminder for us dog owners to remain vigilant about our pet’s dental health. In conclusion, recognizing and treating gingivitis in dogs is essential not just for a fresh breath but for the comprehensive health and happiness of your pet. It’s time to pick up that toothbrush and get proactive!
Causes of Gingivitis in Dogs
Poor Dental Hygiene
One of the primary causes of gingivitis in dogs is simply poor dental hygiene. Just like in humans, maintaining your furry friend’s oral health is vital in preventing the buildup of bacteria that cause inflammation in the gums. When neglected, your dog’s mouth can become a breeding ground for harmful organisms. Consider this: dogs are not always equipped to groom themselves properly when it comes to their teeth. Many dog owners would still happily share their meals with a pup’s eager, slobbery kisses, but they may not realize the importance of regular dental care. Failing to brush your dog’s teeth can lead to a host of oral issues. Here are a few key points to remember regarding dental hygiene:
- Frequency of Brushing: Aim to brush your dog’s teeth at least two to three times a week. Daily brushing is optimal for keeping plaque at bay.
- Dental Products: Use toothpaste and brushes designed specifically for dogs. Human toothpaste can be harmful to them.
- Routine Check-ups: Regular veterinary visits are crucial. A quick dental exam can catch early signs of gingivitis before it worsens.
Plaque and Tartar Build-up
Alongside poor dental hygiene, the accumulation of plaque and tartar is another significant contributor to gingivitis in dogs. When food particles mix with saliva and bacteria, plaque forms on your dog’s teeth. If not removed, it hardens into tartar, making it much more challenging to clean and leading to gum inflammation. Let’s break it down:
- Plaque Formation: This soft, sticky film can develop within 24 hours of brushing. If you notice a light yellow film on your dog’s teeth, that’s plaque starting to accumulate!
- Tartar Development: Tartar is the calcified form of plaque and can be brown or yellow in color. Once it sets in, it requires professional dental cleaning to remove.
I once neglected my own dog’s dental care, and after a couple of months, the vet revealed he had developed substantial tartar—leading directly to gingivitis. From that point on, I vowed never to overlook my dog’s dental hygiene again! In essence, prioritizing your dog’s dental hygiene and managing plaque and tartar can play a significant role in preventing gingivitis and ensuring a healthy mouth. Regular care will not only keep those kisses sweet but also contribute to your dog’s overall health.
Symptoms of Gingivitis in Dogs
Bad Breath
One of the most noticeable symptoms of gingivitis in dogs is bad breath, also known scientifically as halitosis. You may find yourself recoiling from those once-sweet puppy kisses that are suddenly carrying a strong, unpleasant odor. This change in breath is often one of the first indications that something isn’t quite right in your dog’s mouth.
- Why It Happens: Bad breath typically occurs due to the accumulation of bacteria in the mouth. When plaque forms and irritation arises, it leads to the production of sulfur compounds that contribute to that foul smell.
- A Personal Anecdote: I remember when my buddy, Charlie the Beagle, greeted me at the door with a big, slobbery grin. However, I recoiled in shock from his breath! After a quick trip to the vet, I learned that his bad breath was a telltale sign of gingivitis. It’s amazing how something so small can have a big impact on our pups!
If you notice persistent bad breath in your dog, it’s important to take this symptom seriously as it could indicate developing dental issues.
Swollen or Bleeding Gums
Another alarming sign of gingivitis is swollen or bleeding gums. As the gum tissue becomes inflamed, you may notice changes in color, shifting from a healthy pink to a red or darkened shade. When you gently lift your dog’s lip, pay close attention to:
- Inflammation: Swollen gums can feel soft and puffy, indicating irritation and infection.
- Bleeding: You might observe blood on their chew toys, food, or even in their water bowl. If you notice this, don’t hesitate to take action!
- Quick Tips:
- Regularly inspect your dog’s mouth every week.
- Look for signs of discomfort when they eat, chew, or play with toys.
Just like my experience with Charlie, paying attention to these symptoms can help you catch gingivitis before it escalates. After following a consistent dental care routine, Charlie’s breath improved significantly, and his gums returned to their healthy state. It’s crucial to remain vigilant for these symptoms in your dog. Early detection can not only save your pup from discomfort but also help maintain their overall health. A healthy mouth leads to a happy dog!
Diagnosis of Gingivitis in Dogs
Veterinary Examination
When it comes to diagnosing gingivitis in dogs, the first step typically involves a thorough veterinary examination. During this check-up, your veterinarian will look for common signs of dental disease, such as inflammation, plaque, and tartar buildup.
- Visual Inspection: The vet will examine your dog’s mouth, assessing the gums and teeth for any signs of redness, swelling, or infection. A healthy mouth should exhibit pink gums without any flair of inflammation.
- Behavior Assessment: Your vet may ask about your dog’s eating habits, chewing behaviors, and any unusual signs, like favoring one side of the mouth. This information can provide valuable insights into your dog’s oral health.
When I brought my dog Bella in for a routine check-up, I was surprised when the vet pointed out some early signs of gingivitis, despite my regular brushing routine. It was a good wake-up call about how even subtle changes can lead to bigger problems.
Dental X-Rays
If gingivitis is suspected, your veterinarian might recommend dental X-rays to get a clearer picture of your dog’s oral health. The X-rays help reveal issues that may not be immediately visible to the eye.
- Why X-Rays Are Important: X-rays can show the extent of gum disease, damage to the bone surrounding the teeth, and any potential tooth root problems. Some cases of gingivitis can progress to periodontal disease, and X-rays can identify how much damage has occurred below the gum line.
- Preventive Insight: Performing X-rays can also help determine if your dog might need more extensive treatment, such as cleanings or even tooth extractions.
In my experience, when the vet suggested dental X-rays for Bella, I was initially nervous. However, they provided critical insight that helped us address her gingivitis effectively. By catching issues early, we prevented any serious complications from developing. In conclusion, a solid diagnosis is fundamental in managing gingivitis in dogs. With routine veterinary examinations and potentially necessary dental X-rays, you can ensure that your dog receives the comprehensive dental care they deserve, setting the stage for a healthier and happier life. Remember, being proactive today can lead to a brighter, healthier future for your canine companion!
Treatment Options for Gingivitis in Dogs
Professional Dental Cleaning
Once a diagnosis of gingivitis is confirmed, professional dental cleaning is often the first line of treatment. This procedure typically requires sedation to ensure that your furry friend remains still and comfortable while the vet addresses their dental hygiene.
- What It Involves: During a professional cleaning, the veterinarian will carefully remove plaque and tartar both above and below the gum line. They may also polish your dog’s teeth to help prevent future buildup.
- Benefits: Professional cleaning not only eliminates the current issues but also gives your vet a chance to closely inspect your dog’s mouth, identifying any other potential concerns.
I’ll never forget when my dog Daisy underwent her first professional cleaning. I was nervous about anesthesia, but the vet reassured me that it would help her feel more at ease during the process. After the cleaning, Daisy’s breath was fresher, and her energy seemed to bounce back. It was evident that this step was crucial for her overall well-being.
Antibiotics and Medications
In some cases, your veterinarian may prescribe antibiotics and other medications as part of the treatment plan. This approach is particularly helpful when there’s an underlying infection or if the gingivitis has progressed significantly.
- Antibiotics: These can help combat the infection in your dog’s gums and fend off any harmful bacteria that may have entered the bloodstream due to gum disease. They are typically administered for a set period.
- Pain Relief: Occasionally, pain relief medications may also be prescribed to make your dog more comfortable, especially if there is significant gum inflammation or sensitivity.
During Daisy’s treatment, her vet suggested antibiotics alongside her dental cleaning. I noticed a marked difference in her overall demeanor within a few days—her appetite returned, and her usual playful nature was back! In summary, treating gingivitis effectively involves a combination of professional dental cleaning and possible use of antibiotics or other medications. By taking these steps, you can ensure your dog recovers quickly and that their dental health is restored. A healthy mouth leads to a happy pup, so don’t hesitate to consult your veterinarian if you suspect any issues!
Home Care for Dogs with Gingivitis
Brushing Your Dog’s Teeth
After your dog has undergone treatment for gingivitis, maintaining good oral hygiene at home is essential. One of the most effective ways to do this is by regularly brushing your dog’s teeth. It may sound daunting at first, but with patience and the right tools, it can become a bonding routine for both you and your pup.
- Getting Started: Choose a toothbrush and toothpaste specifically designed for dogs. Human toothpaste contains xylitol, which is toxic to pets.
- Establish a Routine: Aim to brush your dog’s teeth at least two to three times a week, if not daily. Consistency helps reduce plaque buildup and keeps gums healthy.
- Tips for Success:
- Begin slowly by letting your dog sniff or lick the toothpaste.
- Gradually introduce the toothbrush, starting with just one tooth, and work your way up to all of them.
I remember the first time I tried brushing Bella’s teeth. She wasn’t keen on it, and the first attempt was mostly toothpaste drool. However, after a few sessions, she started to recognize brushing time as a special event—or perhaps she just loved the peanut butter-flavored toothpaste!
Using Dental Chews and Toys
In addition to regular brushing, dental chews and toys can significantly aid in your dog’s oral health. These products are designed to help reduce plaque and tartar while providing a fun and engaging activity for your furry friend.
- Types of Dental Chews:
- Look for chews that bear the Veterinary Oral Health Council (VOHC) seal. They’ve been approved for effectively reducing plaque and tartar.
- Consider rawhide alternatives or natural chews like carrots, which can also be beneficial.
- Dental Toys: Invest in durable toys that promote chewing and help clean teeth while your dog plays. Look for toys with nubs and textures designed to massage gums and remove debris.
After Daisy’s treatment, I incorporated dental chews into her routine, and she absolutely loves them! They keep her busy and are a tasty way to promote good dental hygiene. It’s amazing how something so enjoyable can have such significant health benefits. In conclusion, home care is vital in managing gingivitis in your dog. By brushing their teeth regularly and providing dental chews and toys, you’ll not only promote better oral health but also enhance your dog’s quality of life. Happy teeth lead to a happy pup, so make dental care a fun part of your daily routine!
Prevention of Gingivitis in Dogs
Regular Vet Check-ups
One of the best defenses against gingivitis in dogs is scheduling regular veterinary check-ups. Just as we keep an eye on our own dental health, it’s essential to ensure your canine companion is on the right track.
- Why Check-ups Matter: During these appointments, your vet can conduct thorough dental examinations, identifying early signs of gum disease before they escalate. Catching gingivitis early is key to preventing further complications.
- Frequency: Aim for at least one veterinary visit per year, although biannual check-ups are even better if your dog is prone to dental issues. These visits often include professional cleanings, which can significantly help maintain oral health.
Recall a time when I took Bella for her annual check-up; the vet noticed some mild plaque buildup that I hadn’t yet spotted during my at-home inspections. Thanks to that visit, she received a cleaning that day, which saved us from future problems!
Maintaining Good Dental Hygiene
While regular vet visits are vital, daily home care is equally important for preventing gingivitis. Establishing a solid dental hygiene routine can keep your dog’s mouth healthy for years.
- Brushing Teeth: As mentioned before, brushing your dog’s teeth several times a week can significantly reduce plaque formation. Try to make it a fun experience; maybe set aside “brushing time” as a relaxing ritual for both of you.
- Providing Dental Chews: Incorporate dental chews and toys into your dog’s routine to help scrape off plaque and massage their gums while they enjoy themselves. It’s like playtime and dental care rolled into one!
- A Balanced Diet: Feeding your dog a well-balanced diet can promote good dental health. Look for high-quality dog food designed to reduce plaque and tartar buildup.
Having experienced the difference in my dog’s health, I can attest to how proactive measures make all the difference. After implementing these preventive strategies, I’ve witnessed a significant improvement in both Daisy’s oral hygiene and her joyful demeanor. In conclusion, preventing gingivitis in dogs is all about dedication to regular vet check-ups and maintaining good dental hygiene habits at home. Together, these strategies can lead to a long, healthy, and happy life for your furry friend. Remember, a healthy mouth contributes to a happy pup!
Complications of Untreated Gingivitis in Dogs
Periodontal Disease
One of the most significant risks associated with untreated gingivitis in dogs is the progression to periodontal disease. This condition represents a severe stage of gum infection that not only affects the mouth but can also lead to further health complications.
- What Happens: In periodontal disease, the inflammation spreads deeper into the tissues surrounding the teeth, including the jawbone. This can cause the gums to recede, leading to tooth mobility, loss, or even extraction.
- Signs to Watch For: Here are some common signs that your dog may be suffering from periodontal disease:
- Increased bad breath
- Swollen or bleeding gums, especially while chewing
- Change in appetite or reluctance to eat
I once witnessed this firsthand with my neighbor’s dog, Toby. They ignored the early signs of gingivitis, and before long, he developed periodontal disease, requiring several tooth extractions. It was a reminder of how important it is to address dental issues early on.
Systemic Health Issues
Beyond localized oral health concerns, untreated gingivitis can lead to systemic health issues in dogs. The bacteria that thrive in the mouth have the potential to enter the bloodstream, affecting other organs in the body.
- Potential Complications:
- Heart Disease: Bacteria from infected gums can contribute to endocarditis, an infection of the heart valves and lining.
- Kidney Problems: Bacterial infection can filter through the kidneys, potentially causing kidney disease over time.
- Liver Issues: Similarly, the liver can become compromised due to the toxins produced by bacteria in the mouth.
It’s alarming to think how an oversight in dental care can lead to such widespread health problems. I once read about a dog that urgently needed treatment for kidney failure, and the vet traced it back to years of untreated gingivitis. This experience stuck with me and reinforced the importance of regular dental care. In essence, neglecting your dog’s gingivitis can lead to serious complications such as periodontal disease and systemic health issues. Being proactive about their oral health not only keeps their mouth healthy but protects their overall well-being. Always remember, a healthy mouth is a gateway to a healthier, happier life for your beloved pet!
Surgical Treatment for Severe Gingivitis in Dogs
Gingivectomy
In cases where gingivitis has progressed to a more severe stage, surgical intervention may be necessary. One common procedure is a gingivectomy, which involves the surgical removal of infected or inflamed gum tissue. This procedure aims to restore the health of the gums and eliminate pockets where bacteria thrive.
- When It’s Needed: A gingivectomy may be recommended when:
- The gums are excessively swollen or have developed deep pockets.
- There is significant gum recession affecting tooth stability.
- Your dog is not responding to non-surgical treatments.
- Post-Procedure Care: After a gingivectomy, your dog may require a quiet recovery period and a special diet to minimize discomfort. Your vet will likely prescribe pain relievers and may suggest soft food for a few days to aid healing.
I recall a time when my friend’s dog, Max, underwent a gingivectomy. He had been suffering from severe gum disease that didn’t improve with regular cleanings. After the surgery, his owner was amazed by the transformation in his mood and energy. It was as if he had a fresh start, free from the discomfort that had been plaguing him!
Tooth Extraction
Another potential surgical treatment for severe gingivitis is tooth extraction. This procedure is generally indicated when a tooth has become severely affected by periodontal disease or when the root has been compromised.
- Why Extraction?: Tooth extractions become necessary when:
- A tooth is too damaged to save due to deep infection.
- The tooth is causing pain and affecting your dog’s ability to eat.
- The Extraction Process: During the tooth extraction, your dog will be under anesthesia, ensuring they remain comfortable throughout the procedure. Post-surgery, your veterinarian will provide guidelines for pain management and recovery.
I once saw a dog named Bella, who struggled with painful gums. After her tooth extraction, the change in her quality of life was incredible. She resumed playing with her favorite chew toys and even regained her appetite—proof that sometimes, the hardest decisions lead to the best outcomes. In conclusion, while surgical treatments such as gingivectomy and tooth extraction may sound daunting, they can be lifesaving options for dogs suffering from severe gingivitis. By recognizing the need for these interventions and working closely with your veterinarian, you can help restore your pet’s oral health and overall well-being. Remember, a healthy mouth contributes significantly to a happy, vibrant life!
Prognosis and Recovery for Dogs with Gingivitis
Monitoring Your Dog’s Oral Health
Once your dog has received treatment for gingivitis, whether through professional cleaning, surgery, or medication, the journey doesn’t end there. Continuous monitoring of your dog’s oral health is crucial to ensuring that any potential recurrence or complications are caught early.
- Regular Check-Ins: Make it a habit to inspect your dog’s mouth regularly. Look for signs of plaque buildup, inflammation, or unusual behaviors like reluctance to eat or chew.
- Routine Vet Visits: Schedule follow-up appointments with your veterinarian every six months. These visits can catch any early signs of gum disease or other dental issues before they escalate.
I remember after Bella’s gingivitis treatment, I made it a point to check her teeth weekly. One day, I noticed some slight redness in her gums, which prompted me to schedule a vet visit. Thanks to my vigilance, we caught the issue early, and Bella made a smooth recovery.
Long-term Management Strategies
To maintain your dog’s oral health in the long term, it’s essential to implement effective management strategies. These practices can help prevent the return of gingivitis and other dental issues.
- Daily Brushing: Commit to brushing your dog’s teeth daily or at least several times a week. Consistent brushing reduces plaque buildup and keeps gums healthy.
- Dental Chews and Toys: Incorporate dental chews and toys into your dog’s routine to help maintain oral hygiene while also keeping them entertained.
- Balanced Diet: Feed a high-quality diet specifically designed to promote dental health. Look for kibble formulated to help reduce plaque and tartar.
Incorporating these strategies into your dog’s daily life can be beneficial. For example, when I switched Daisy to a dental-specific diet, I noticed her breath improved and her enthusiasm for playtime soared! In summary, the prognosis for dogs treated for gingivitis is generally very favorable with proper care and monitoring. By making oral health a priority through continuous evaluation and effective management strategies, you can help your dog enjoy a lifetime of strong and healthy teeth. Remember, a little effort goes a long way in keeping your furry friend happy and pain-free!
You might also find this article helpful Weight Management: Tips for a Healthy Weight