The Science of Hair Loss: Genetics and Male Pattern Baldness
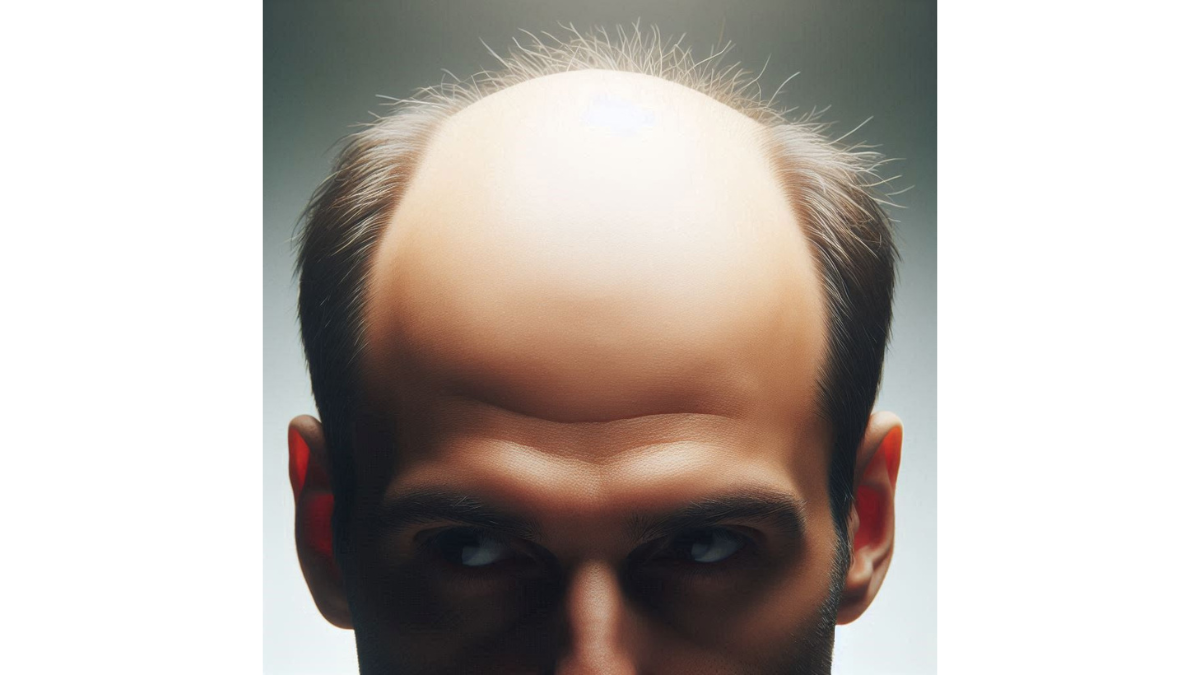

The Science of Hair Loss: Genetics and Male Pattern Baldness – When it comes to understanding hair loss, particularly male pattern baldness, genetics plays a crucial role. You might have noticed that certain traits, like hair type or eye color, are often passed down through generations. Well, hair loss is no different. Research has shown that genetics significantly influences your susceptibility to falling hair. Imagine sitting around a family dinner and noticing the hairlines of your grandfather and father. If they both experienced hair loss, it might not come as a surprise if you’re facing similar challenges. It turns out that male pattern baldness (MPB) is linked to a combination of genes inherited from both parents. So how does this actually happen? The gene that affects hair loss interacts with certain hormones in the body, ultimately leading to the shrinkage of hair follicles over time. This is particularly prevalent in males, as they typically have higher levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone that influences hair follicle behavior.
Understanding Male Pattern Baldness
Male pattern baldness isn’t just a random occurrence; it tends to follow specific patterns of hair loss, primarily beginning at the temples and crown. Knowing this can be quite helpful when you notice some changes. Here are some common indicators of MPB:
- Receding Hairline: This often starts around the temples and expands backward.
- Thinning at the Crown: Hair becomes noticeably thinner, often leading to a bald spot.
- Overall Diffusion: In more advanced stages, hair may thin out significantly across the scalp.
Personal experiences can provide insight into how MPB affects daily life. I recall a friend who started noticing his hair thinning in his late twenties. He often joked about sporting the “distinguished look” that comes with baldness, but in quieter moments, he admitted it affected his confidence. What’s fascinating is how many individuals experience similar feelings and reactions regarding their hair loss. It’s a common struggle—one that can resonate deeply. Taking a step back, understanding MPB is also essential for creating effective treatment strategies. While genetics is a strong determinant, lifestyle factors, dietary habits, and stress levels can also play pivotal roles. Unfortunately, it’s not just about genetics; a combination of factors can expedite or slow down the process. In conclusion, embracing the science of hair loss—particularly the interplay between genetics and male pattern baldness—can lead to a more profound understanding of what one might experience. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and becoming informed is an empowering step toward management or even treatment.
The Role of Genetics in Hair Loss
Genetic Causes of Hair Loss
Transitioning from the understanding of hair loss, it’s essential to delve deeper into the specific genetic causes. What exactly initiates this process? Genetic causes of hair loss can be traced primarily through various markers in your DNA. And while it may sound intimidating, unraveling these genetic threads can provide clarity. The main culprits in genetic hair loss are the androgen receptors (AR) that bind with hormones like testosterone. When these receptors are highly sensitive to hormones, they can unintentionally lead to the miniaturization of hair follicles. This phenomenon results in finer, shorter hair strands until hair production stalls altogether. Here are a few noteworthy genetic factors that contribute to hair loss:
- Family History: A family tree filled with bald heads or thinning hair could indicate that you have a higher likelihood of experiencing hair loss.
- Genetic Variants: Specific gene variations, particularly around the AR gene, can influence the sensitivity of hair follicles to DHT.
- Age: Genes dictate not just the onset but also the progression of hair loss, meaning that even if you’re genetically predisposed, the age of onset may vary widely.
Personal experiences can highlight these trends. For example, a colleague once mentioned how his grandfather’s baldness was a family hallmark. As a result, he always had his hair styled to conceal any hints of thinning. It’s a powerful reminder of how deeply personal and psychological hair loss can be.
Hereditary Factors in Male Pattern Baldness
Shifting our focus specifically to male pattern baldness, we find that hereditary factors significantly exacerbate the condition. Unlike generalized hair loss, male pattern baldness tends to display a unique inheritance pattern, primarily influenced by both parental genetics. Here’s why hereditary factors matter:
- Y-Chromosome Link: Male pattern baldness is often linked to the X and Y chromosomes, hinting that men inherit specific genes contributing to baldness from their mothers as well.
- Polygenic Nature: This implies multiple genes work together, rather than a single gene causing baldness, making it a complex hereditary trait.
Consider an uncle who struggles with hair loss—you might have inherited those same vulnerable genes. Recognizing these hereditary factors can help you manage expectations and help you prepare for potential hair loss. Moreover, acknowledging the hereditary aspects can also be a bonding opportunity. Conversations about hair loss might lead to shared stories within families, creating a collective experience that can normalize individual feelings. In summary, the genetic underpinnings of hair loss and hereditary factors significantly shape individual experiences with male pattern baldness. By understanding these aspects, you empower yourself to make informed choices about prevention and treatment, recognizing that genetic elements are just one piece of a broader puzzle.
Mechanisms of Male Pattern Baldness
Hormonal Influence on Hair Loss
As we unravel the complexities of male pattern baldness, it’s essential to consider the hormonal influence at play. Hormones significantly affect hair growth, and understanding how they interact with hair follicles can illuminate why hair loss occurs for many men. The primary hormone linked to hair loss is dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This is derived from testosterone through the action of an enzyme called 5-alpha reductase. When DHT binds to androgen receptors in hair follicles, it can trigger a response that leads to follicle miniaturization. This process shrinks the hair follicles gradually, producing shorter and finer hairs—eventually halting hair growth altogether. Here are a few key points about hormonal influence:
- DHT Sensitivity: Not all hair follicles are equally sensitive to hormones. Those on the scalp can be more susceptible, leading to localized hair thinning.
- Age Factor: As men age, testosterone levels fluctuate, leading to increased DHT levels, which can intensify hair loss.
Think of it this way: a friend of mine, who always had a full head of hair, started noticing some significant thinning in his early 30s. After a consultation, he learned that elevated DHT levels were wreaking havoc on his hair follicles. Understanding the hormonal influence provides insight into effective treatment protocols. For example, medications like finasteride work by blocking the conversion of testosterone to DHT, which can help slow down hair loss for some individuals.
Genetics and Hair Follicle Sensitivity
Transitioning to the genetic aspects, we find that the sensitivity of hair follicles to hormones is crucial in understanding male pattern baldness. As previously mentioned, genetics heavily influence how susceptible your hair follicles are to the effects of DHT. The genetic predisposition towards heightened follicle sensitivity means that some individuals experience hair loss earlier or more severely than others. Here’s what you should know:
- AR Gene Variability: Variations in the androgen receptor (AR) gene can lead to differing responses to DHT among individuals. This might explain why baldness appears in some family members but not in others, even when they share bloodlines.
- Gene Interactions: Male pattern baldness is influenced by several genes working together rather than a single culprit. This polygenic nature complicates the predictability of hair loss onset and severity.
Reflecting on personal experiences, I recall a family gathering where everyone shared hair stories. One cousin pointed out that his rapid hair loss mirrored that of his father’s and uncle’s. It was a lighthearted discussion, but it highlighted how genetic factors create a shared narrative within families. Overall, the mechanisms of male pattern baldness are multi-faceted, involving hormonal processes and genetic influences that affect hair follicle sensitivity. By grasping these mechanisms, you’re not only better equipped to understand your own hair loss journey but also to consider targeted treatment options tailored to your unique genetic and hormonal profile.
Genetic Testing for Hair Loss
DNA Analysis for Hair Loss
As we delve deeper into the science surrounding male pattern baldness, it becomes increasingly fascinating to explore the role of genetic testing. DNA analysis has emerged as a powerful tool, allowing you to peek into your genetic makeup to understand your predisposition to hair loss. The process is surprisingly straightforward. Many companies now offer at-home DNA testing kits. You simply provide a saliva sample, and the lab conducts an analysis to identify specific genetic markers associated with hair loss. These markers can inform you about your potential risk for male pattern baldness. Here are a few reasons why DNA analysis for hair loss can be beneficial:
- Personalized Insights: Rather than relying solely on family history, you can gain a clearer picture of your genetic predisposition.
- Informed Decisions: Knowing your risk level can guide lifestyle choices and treatment options tailored to your situation.
- Awareness: Empowering yourself with knowledge can reduce anxiety and help you approach hair loss proactively.
For instance, one of my friends recently decided to undergo this testing out of curiosity. He had seen relatives struggle with thinning hair and wanted to determine if it was in his future. Upon receiving his results, he learned that he did have several genetic markers linked to hair loss. This knowledge helped him start researching preventive strategies and treatment options earlier, which gave him a sense of control over his timeline.
Predicting Risk of Male Pattern Baldness
Now, let’s talk about the important aspect of predicting the risk of male pattern baldness through these genetic insights. Understanding the likelihood of developing MPB isn’t just about family histories or societal myths; it can also be scientifically quantified through genetics. Based on your DNA analysis, you might receive a risk score that predicts how likely you are to experience hair loss. Here’s what you need to know:
- Age Factor: Genetic testing can indicate not only if you’re at risk, but also potentially when you might start noticing changes.
- Tailored Preventive Measures: By knowing your risk level, you can discuss tailored treatment plans with your healthcare provider focused on proactive measures, such as lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, or medical interventions.
I recall a friend who, upon discovering his elevated risk for male pattern baldness, made swift changes to his lifestyle. He started focusing more on nutrition and stress management, leading to better overall hair health. In summary, genetic testing for hair loss through DNA analysis opens new doors for understanding and managing male pattern baldness. Instead of feeling blindsided by hair loss, you can take informed steps tailored to your genetic makeup and risk profile. It’s an empowering experience that encourages proactive management of a condition that affects so many men today.
Treatment Options for Male Pattern Baldness
Medications for Hair Loss
As we journey through the landscape of male pattern baldness, understanding the various treatment options is essential. When it comes to managing hair loss, medications are often the first line of defense, and they can be quite effective for many men. Two primary medications are commonly prescribed for hair loss:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): This topical solution is applied directly to the scalp. It works by stimulating hair follicles and increasing blood flow to the area. Many users report visible results with consistent application, typically after several months.
- Finasteride (Propecia): This oral medication tackles hair loss by inhibiting the conversion of testosterone to DHT, the hormone primarily responsible for follicle shrinkage. Studies have shown that finasteride can slow hair loss and even promote regrowth in some men.
Personal anecdotes can often shed light on these treatments. A friend of mine started using minoxidil after noticing thinning hair in his late twenties. Initially skeptical, he applied the solution faithfully every day. To his amazement, after six months, he noticed a thicker hairline and less hair on his pillow each morning. His confidence soared, allowing him to flaunt his hair rather than hide it. However, it’s important to consider the potential side effects of these medications, such as scalp irritation with minoxidil or sexual side effects with finasteride. Always consult a healthcare professional to discuss the best eating and weaving these options into your treatment plan.
Surgical Interventions for Baldness
If medications aren’t your preferred route or if you’re looking for more drastic measures, surgical interventions are available. These procedures can provide significant, lasting results for those facing more extensive hair loss. Two popular surgical options include:
- Hair Transplantation: This involves taking hair follicles from areas of the scalp with healthy hair (often the back or sides) and implanting them into thinning or bald areas. Follicular unit extraction (FUE) and follicular unit transplantation (FUT) are two common methods. Many men find this procedure restores not only their hair but also their confidence.
- Scalp Reduction: This procedure involves removing bald areas of the scalp and pulling down the hair-covered scalp to fill the gap. Though less common today than hair transplants, it can be an option for individuals with distinct patterns of baldness.
I once attended a wedding where I met a former classmate who had undergone a hair transplant. He exhibited a full head of hair, which he styled proudly. During our conversation, he shared how the procedure not only transformed his appearance but significantly boosted his self-esteem. In conclusion, the treatment landscape for male pattern baldness is diverse, offering both medication and surgical options to cater to different needs and preferences. Whether you choose to go the medical route or consider surgical interventions, what’s important is understanding the options available to you and taking proactive steps towards maintaining your hair health. As men navigate this common journey, the right treatment can empower them to embrace their appearance with renewed confidence.
Lifestyle and Preventive Measures
Diet and Hair Health
As we explore the holistic approach to managing male pattern baldness, it’s essential to recognize the role of lifestyle choices, particularly diet. What you put on your plate can significantly influence hair health, and the right nutrients can help strengthen your locks and even slow down the loss process. Incorporating certain foods into your diet can be transformative. Here are some key nutrients and examples of foods that can promote hair health:
- Proteins: Hair is primarily made of a substance called keratin, which is a protein. Foods rich in protein, such as eggs, fish, and lean meats, can provide the necessary building blocks for healthy hair.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These can help nourish hair follicles and promote blood circulation. You can find them in fatty fish like salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds.
- Vitamins A and C: These vitamins play a crucial role in producing sebum, an oily substance that keeps hair healthy. Include foods like carrots (Vitamin A) and oranges (Vitamin C) in your diet.
- Zinc and Iron: Deficiencies in these minerals can lead to hair loss. Foods like spinach for iron and pumpkin seeds for zinc can help bolster your intake.
I remember when a friend decided to overhaul his diet after noticing some thinning. He replaced processed snacks with a variety of hair-friendly foods, from avocados to nuts. Within months, not only did he feel more energetic, but he also noticed a positive change in his hair’s overall health and shine. What you eat matters, and making these changes could be a step toward not only retaining your hair but also improving your overall health.
Managing Stress and Hair Loss
Transitioning to another significant factor, managing stress levels is pivotal when addressing hair loss. Chronic stress can lead to various physical health issues, including hair problems. When you’re stressed, your body produces hormones like cortisol, which can negatively affect hair follicles and trigger hair shedding. Here are some effective strategies to help manage stress and its potential impacts on your hair:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can help reduce stress and improve blood circulation. Whether it’s a brisk walk, yoga, or hitting the gym, find an activity you enjoy.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Incorporating mindfulness practices into your daily routine can calm your mind. Even a few minutes a day can make a difference in how you manage stress.
- Sleep Hygiene: Ensure you prioritize sleep, as lack of rest can exacerbate stress levels. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Social Connections: Engaging with friends or family can serve as a great stress reliever. Sharing experiences and simply talking can help lighten your emotional load.
I once found myself feeling overwhelmed due to work pressures affecting my hair. I started practicing meditation and made a commitment to regular exercise. Gradually, I noticed not just a calmer mindset but a marked improvement in my hair’s resilience. In conclusion, adopting a holistic approach to hair health, focusing on diet and stress management, can be significant in reducing your risk of male pattern baldness. By cultivating healthy lifestyle habits that encompass nutrition and mental well-being, you empower yourself to take control of your hair health and overall quality of life.
Future Research and Developments
Advances in Genetics and Hair Loss
As we look ahead in the realm of male pattern baldness, promising advances in genetics are paving the way for new understanding and treatment options. The intersection of genetics and hair loss research is expanding, providing insights that previously seemed like mere speculation. Recent studies have delved deeper into understanding the genetic markers associated with hair loss. Scientists are beginning to identify specific genes linked not just to susceptibility, but also to the severity and progression of baldness. This newfound knowledge could be game-changing for anyone concerned about hair loss. Here are some exciting developments in this area:
- Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS): These studies examine genetic variations across large populations to identify connections between specific genes and traits like hair loss. They’ve already uncovered several new genetic loci associated with male pattern baldness.
- Personalized Medicine: With greater understanding of genetic predispositions, there’s potential for personalized treatment plans tailored specifically to individuals’ genetic profiles.
I recently came across an article highlighting a research team focused on how genetic variants could guide hair loss treatments. This not only opened up avenues for more effective solutions but also inspired hope for individuals tired of blanket solutions.
Potential Gene Therapies for Baldness
Moreover, the field is also exploring the transformative potential of gene therapies in treating baldness. Imagine a scenario where gene therapy could target the very roots of the problem, offering a biological reset for hair follicles. Here are a few concepts that researchers are exploring:
- Gene Delivery Systems: Techniques involve delivering specific genes into hair follicles to enhance their growth potential. This could mean introducing genes that encourage follicle activity or block pathways that lead to hair loss.
- CRISPR Technology: This revolutionary gene-editing technology could allow scientists to edit specific genes linked to hair loss. There is incredible potential for CRISPR to target faulty genetic pathways that are responsible for male pattern baldness.
- Stem Cell Therapies: Future treatments may involve using stem cells to regenerate hair follicles. Research is ongoing into the viability of stem cell transplants as a solution to baldness, suggesting a fascinating avenue for regenerative medicine.
While these therapies are still in the experimental phases, they represent a promising horizon for those struggling with hair loss. Just imagining walking into a clinic where a quick gene therapy could encourage hair regrowth feels almost sci-fi, yet it may not be far from reality. In conclusion, as we advance into the future, the ongoing research in genetics and potential gene therapies presents exciting possibilities for treating male pattern baldness. By understanding the genetic foundations of hair loss and harnessing technology to manipulate those pathways, we may soon witness a revolution in how we address this common yet challenging issue. Taking proactive interest in these developments could empower individuals to seek solutions that go beyond what is currently available, ultimately leading to a more confident tomorrow.
You might also find this article helpful Building a Strong Foundation :Balanced Diet Enhances Your Health